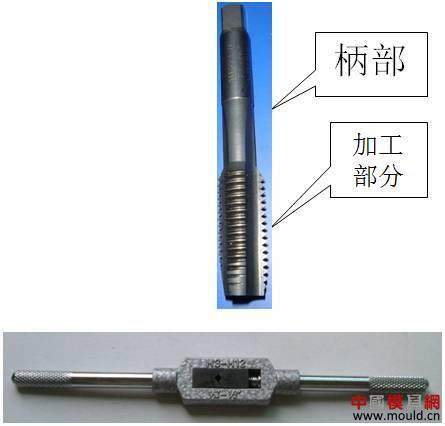
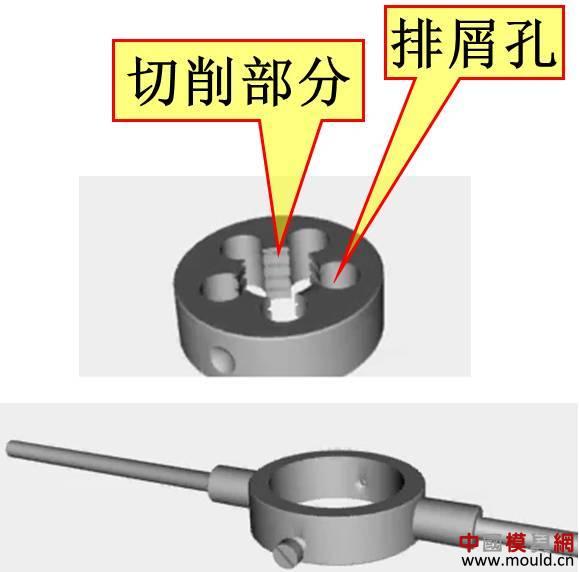
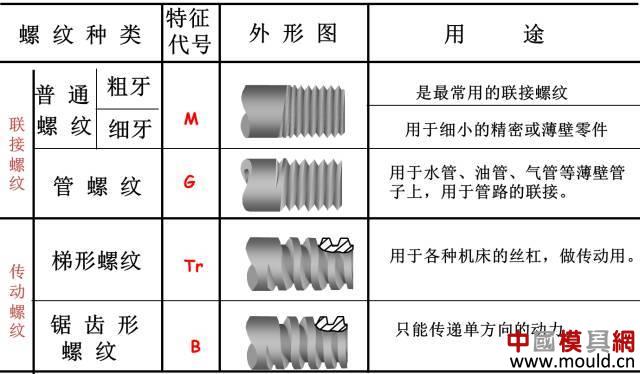
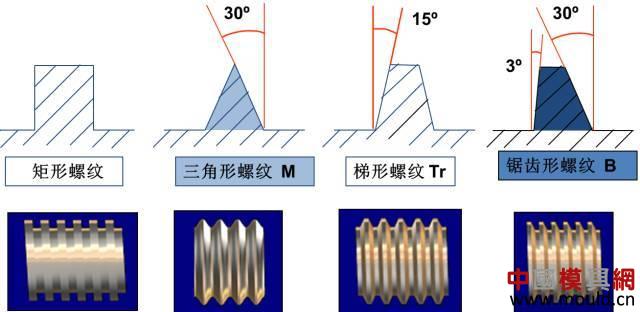
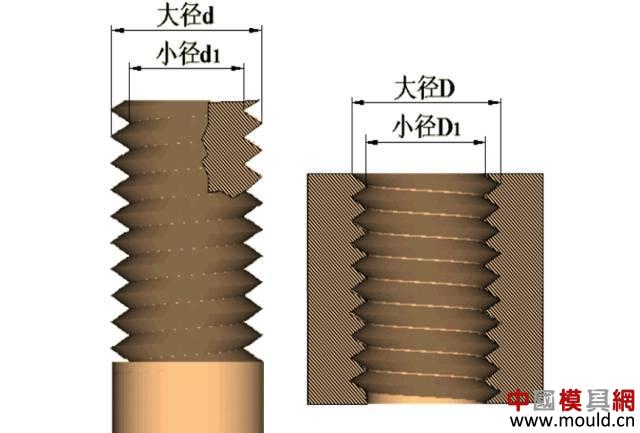
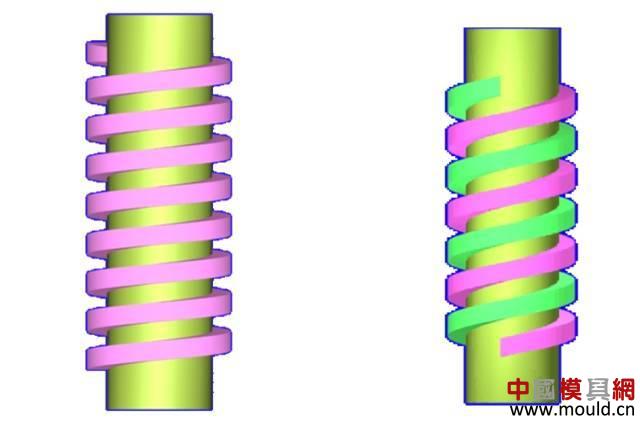
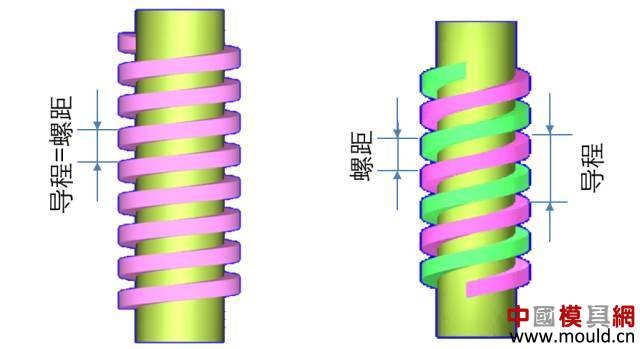
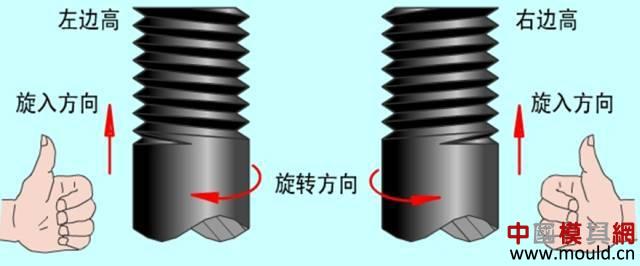
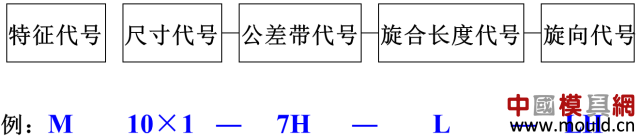
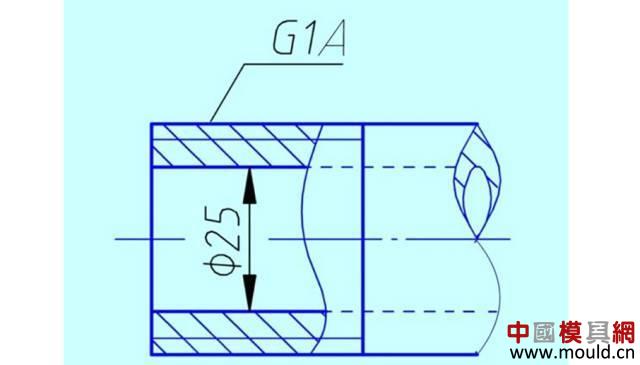
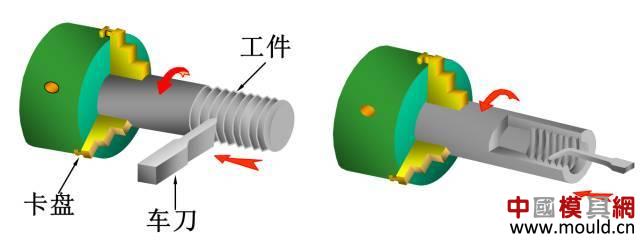
First, the type of thread According to the tooth type, it can be divided into triangle, trapezoid, rectangle, zigzag and arc thread; According to the direction of the thread, it can be divided into left-handed and right-handed; According to the number of spiral lines can be divided into single line and multi line; According to the shape of the thread parent, it is divided into a cylinder and a cone. Second, the elements of the thread The thread consists of five elements: tooth shape, nominal diameter, number of lines, pitch (or lead), and direction of rotation. Tooth type On the cross-sectional area through the thread axis, the contour shape of the thread is called a tooth shape. There are triangles, trapezoids, zigzags, arcs and rectangles. Thread type comparison: 2. Diameter The thread has a large diameter (d, D), a medium diameter (d2, D2), and a small diameter (d1, D1). The nominal diameter is used when indicating the thread, and the nominal diameter is the diameter representing the thread size. The nominal diameter of a common thread is the large diameter. External thread (left) internal thread (right) 3. Number of lines A thread formed along one spiral is called a single thread, and a thread formed by two or more spirals equidistantly distributed in the axial direction is called a multi-thread thread. Single thread (left) double thread (right) 4. Pitch and lead The pitch (p) is the axial distance between two points on the median diameter of two adjacent teeth. The lead (ph) is the axial distance between two adjacent points on the same diameter line on the same spiral line. For single thread, lead = pitch; for multi-thread threads, lead = pitch x number of lines. 5. Rotation The thread that is screwed in when rotating clockwise is called a right-hand thread; The thread that is screwed in when it is rotated counterclockwise is called a left-hand thread. Left-handed thread Third, the mark of the thread (1) ordinary thread Ordinary threads are the most widely used, and the threads on threaded fasteners (bolts, studs, screws, nuts, etc.) are generally ordinary threads. Ordinary thread is divided into coarse thread and normal thread. Fine-toothed common threads are mostly used on precision parts and thin-walled parts. In the marking of the thread, the pitch of the fine thread of the fine tooth must be injected, and the pitch of the ordinary thread of the coarse tooth is generally not marked. The mark of a common thread consists of five parts: 1) Feature code M (for ordinary thread) 2) Size code Dimension code: nominal diameter × pitch (the lead and pitch of the multi-thread thread are to be injected, the common thread pitch of single-line coarse teeth is not marked). “M10†means a single thread coarse thread with a nominal diameter of 10 mm and a pitch of 1.5 mm. “M10×1†means a single-threaded fine thread with a nominal diameter of 10 mm and a pitch of 1 mm. 2) tolerance mark code of ordinary thread It consists of the tolerance level (number) and the basic deviation (the external thread is indicated by a lowercase letter and the internal thread is indicated by a capital letter), for example, 5g6g, 6g, 6H, 7H. When the thread diameter tolerance zone and the top diameter tolerance zone code are different, they must be separately injected, such as: M10-5g 6g When the middle diameter and the top diameter tolerance band code are the same, only one code number is used, such as: M10×1-7H The tolerance band code is 6g or 6H (nominal diameter ≥ 1.6mm) and is not marked. 3) The length of the common thread There are three types: long, medium and short, which are denoted by codes L, N and S respectively. M10-5g6g-S is a thread with a short twist length M10-7H-L is a thread with a long twist length When the thread is of medium rotation length, the code N is not marked. When special needs are made, the value of the length of the screw can be indicated. M20×2-5g6g-40 4) Swirling code Mark LH when left-handed and not mark when right-handed. M10-7H-L-LH is left-hand thread M10-7H-L is right-hand thread (2) pipe thread Pipe threads are generally used in the connection of pipes (water pipes, oil pipes, gas pipes, etc.). The marking of the pipe thread is marked by the method of guiding, and the guiding wire points to the large diameter of the thread. Pipe thread marking: It consists of thread feature code, size code and direction of rotation. The size code is not the size of the large diameter of the thread, but the size of the pipe (inch). Those that are not marked in the mark are right-handed. Example of a 55° unsealed pipe thread marking: G: thread feature number of unsealed pipe thread; G3/4: single-line right-handed cylindrical internal thread with size code 3/4; G3/4A or G3/4B: single-line right-handed cylindrical external thread with size code 3/4, A and B in the mark are the tolerance level of the thread diameter; The LH in G3/4LH and G3/4A-LH represents a left-handed thread, and the thread pair formed by the two only labels the external thread. Example of a 55° seal pipe thread marking: Rp3/4LH: single-line left-handed cylindrical internal thread with size code 3/4; Rc3/4: single-line right-handed conical internal thread with size code 3/4; Rp/R13/4 LH and Rc/R23/4: The internal thread and the external thread are screwed together to form a thread pair. Rp: the thread feature code of the internal thread of the sealing cylinder; Rc: the thread feature code of the internal thread of the sealing cone; R1: characteristic code of the external taper thread matched with the internal thread of the cylinder; R2: characteristic code of the conical external thread matched with the internal thread of the cone; (3) trapezoidal thread and zigzag thread Trapezoidal threads and zigzag threads are commonly used on screw bars that transmit motion and power. When the trapezoidal thread is working, both sides of the tooth are stressed, and the zigzag thread is forced by one side when working. The trapezoidal and zigzag threads are marked the same as normal threads. Example of a trapezoidal thread mark: Tr40×7LH-7e, trapezoidal thread (thread feature code Tr), nominal diameter φ40, single wire, pitch 7, left-handed, medium-diameter tolerance with code 7e; medium-threaded length. Note: Only the medium-diameter tolerance band code is marked. There are only two kinds of screw-in lengths (codes N and L). When the length is equal, N is omitted. When the thread is a multi-thread thread, it is marked as: Tr40×14(P7)-7e, where “14†is the lead and “7†is the pitch and double thread. The thread pair of the trapezoidal thread is expressed as: Tr40×7-7H/7c, the tolerance of the internal thread is in the front, and the tolerance of the external thread is in the back, separated by “/â€. Fourth, thread processing 1, tapping thread and sleeve thread Tapping: A method of machining an internal thread with a tap in a hole is called tapping. The formula for calculating the diameter of the bottom hole: considering the plasticity of the material. For steel and plastic material: D hole = DP D hole: thread bottom hole diameter D: internal thread diameter P: pitch Example: What is the diameter of the bottom hole for the M10 thread on the steel? According to the formula D hole = DP = 10 - 1.5 = 8.5mm For cast iron and small plastic materials: D hole = D-(1.05~1.1)P Example: What is the diameter of the bottom hole when we want to attack the M10 thread on cast iron? According to the formula D hole = D - (1.05-1.1) × 1.5 = 8.35 ~ 8.42mm Set of threads: The method of cutting an external thread on a round rod or tube with a die is called a sleeve thread. The formula for calculating the diameter of the round rod: d rod = d-0.13P d rod: set of threaded front round rod diameter, mm d: thread diameter, mm p: pitch, mm Example: We want to make a screw for M10. What is the diameter of the round rod used? Should be according to the formula d rod = d-0.13P =10-0.13×1.5=9.8mm 2. Thread External thread and internal thread -End- Polycarbonate Solid Sheet ,Solid Polycarbonate Roofing Sheets,Clear Solid Polycarbonate Sheet,4Mm Solid Polycarbonate Sheet NINGBO CHAOMEI PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.pcban88.com