welding boiler plate,boiler steel plate low price,high quality boiler plate,boiler plate grade Shandong Fengbao Metal Products CO.,LTD. , https://www.fengbaosteels.com
What is the difference between a Gigabit Ethernet cable and a 100M Ethernet cable?
What is the difference between a Gigabit Ethernet cable and a 100M Ethernet cable?
Gigabit network cables refer to network cables suitable for Gigabit networks, and 100M network cables are network cables suitable for 100M networks. According to specific cables, Gigabit network cables refer to Category 6 network cables and Category 5 network cables. The 100M Ethernet cable refers to five types of network cables.
Super Category 5 network cables are generally applied to 100M network cables to achieve the connection between desktop switches and computers. If Category 5 network cables are used as Gigabit network cables, the required accessories are expensive and the cost is relatively high. When used in a gigabit network, a Category 6 cable is used instead of a Category 5 cable. The Category 6 cable is compatible with 100M networks.
If the 100M network has a plan to upgrade the Gigabit network, it is recommended to use Category 6 network cables. You do not need to re-arrange the network cables when upgrading the network.
In the 100M network, the network cable only uses orange-white--1, orange-2, green-white-3, and green-6 in the process of transmitting network signals. That is to say, even other 4 wire cores are not needed, and network signals can be transmitted under 100M network.
Although in theory 100M networks should also use 8-core network cables to maintain long-distance stable transmission, at present, most routers still only have four contacts to identify the network cables, and they have not caused any serious problems during the transmission process. Big question.
In a Gigabit network, the network cable uses 8 cores when transmitting network signals. The four cores of the network cable cannot achieve simultaneous transmission and reception of the Gigabit network, that is, the four cores can only realize Gigabit network reception. Data or sending data, both of which cannot be performed simultaneously. When transmitting a Gigabit network, a Gigabit router is also required (the 8 sockets have contacts).
Difference between Category 5 and Category 6 network cables
Category 5 line: Category 5 has less attenuation and less crosstalk. Compared with category 5, it has a higher attenuation to crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (StructuralReturn Loss), smaller delay errors, and performance is very Greatly improved.
Category 6 cable: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz ~ 250MHz. Category 6 cabling system should have a large margin at 200MHz, and it provides 2 times the bandwidth of Category 5. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than the Category 5 standard, and it is suitable for applications with transmission rates higher than 1Gbps.
An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5 is that it improves the performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss. For new generation full-duplex high-speed network applications, excellent return loss performance is extremely important. The basic link model is cancelled in the six types of standards. The wiring standard adopts a star topology. The required wiring distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90m, and the channel length cannot exceed 100m.
The difference between Category 5 and Category 6 cables is their internal structure and performance.
The internal structure of a Category 5 cable is only 4 pairs of twisted pair Copper wires.
Type 6 network cables have a cross skeleton on the inside structure, which is mainly to reduce crosstalk between pairs and reach the standard of type 6 network cables. Most of the type 6 network cables have a cross skeleton, and a small number of cables can meet the standard of category 6 cables. Is a single skeleton or no skeleton.
How to distinguish between 100M and Gigabit by equipment
As shown in the following figure, each network port has two left and right green lights. The left side is on at 100M, the right side is on 10M, and both on are on 1000M devices. Of course, the switch, network cable, and equipment connected to the switch all support 1000M, and this 1000M will be on.
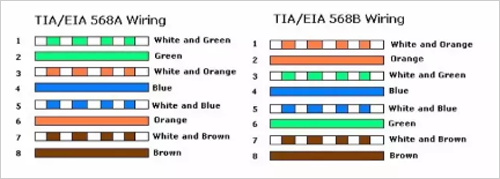
Fourth, the difference between the cross connection method of 100M and Gigabit network cables
One end is: 1 orange white, 2 orange, 3 green white, 4 blue, 5 blue white, 6 green, 7 brown white, 8 brown (568B)
The other end: 1 green white, 2 green, 3 orange white, 4 brown white, 5 brown, 6 orange, 7 blue, 8 blue white (not 568A)
5. Is the crystal head of the 100M Ethernet cable the same as the Gigabit Ethernet cable?
If you use a Gigabit Ethernet cable, use a Gigabit crystal head. Many people will ignore this and think that the crystal head is the same. In fact, there are differences, as shown in the figure: 100M on the left and Giga on the right. You can see that there are differences in structure between 100M and Gigabit.
In terms of specifications, the ultra-category five and six category network cables are the same in size and material. However, the size of the copper cores of Category 5 and Category 6 network cables is different.
The size of the copper core of the super-type 5 network cable is about 0.45 to 0.51, and the size of the copper core of the type 6 network cable is about 0.52-0.58. The copper core of Category 6 network cable is thicker than that of Category 5 network cable. Because the copper cores of the two are different, the holes inside the crystal head are also different.
The crystal heads of the six types of network cables are arranged in different layers, that is, they are divided into two rows, four above, and four below. The crystal heads of the super five types of network cables are arranged in a straight line.
Is the manufacturing method of crystal head for 100M Ethernet cable and Gigabit Ethernet cable the same? The answer is yes, the method is the same.